Suicide prevention for older adults is a pressing public health challenge, yet it often receives insufficient attention and resources. Research indicates that individuals aged 75 and older experience the highest suicide rates among all age groups, underscoring the urgent need for targeted mental health resources that cater specifically to this vulnerable population. Despite this alarming trend, many well-known national organizations overlook elderly suicide prevention in their initiatives, limiting senior mental health support to broader age demographics. As social isolation and loneliness become more prevalent among older adults, the need for effective geriatric suicide awareness and specialized intervention strategies grows more critical than ever. By prioritizing resource availability and outreach in this area, we can help combat the distressing statistics surrounding suicide rates in older adults and foster a more supportive community.
Addressing the complexities of mental well-being among the senior population is increasingly vital in our society. The phenomenon of suicide among the elderly, particularly those isolated or suffering from chronic conditions, highlights an urgent call for intervention. As many older individuals are turning to digital platforms for information, there is a significant gap in accessible and appropriate suiсide prevention initiatives tailored to their needs. Engaging resources and campaigns that focus on senior mental wellness can play a crucial role in mitigating risks and promoting healthier, happier lives. Understanding and alleviating the factors that contribute to late-life suicide is key in forming effective support systems that cater to the unique challenges faced by older adults.
Understanding the Risk of Suicide Among Older Adults
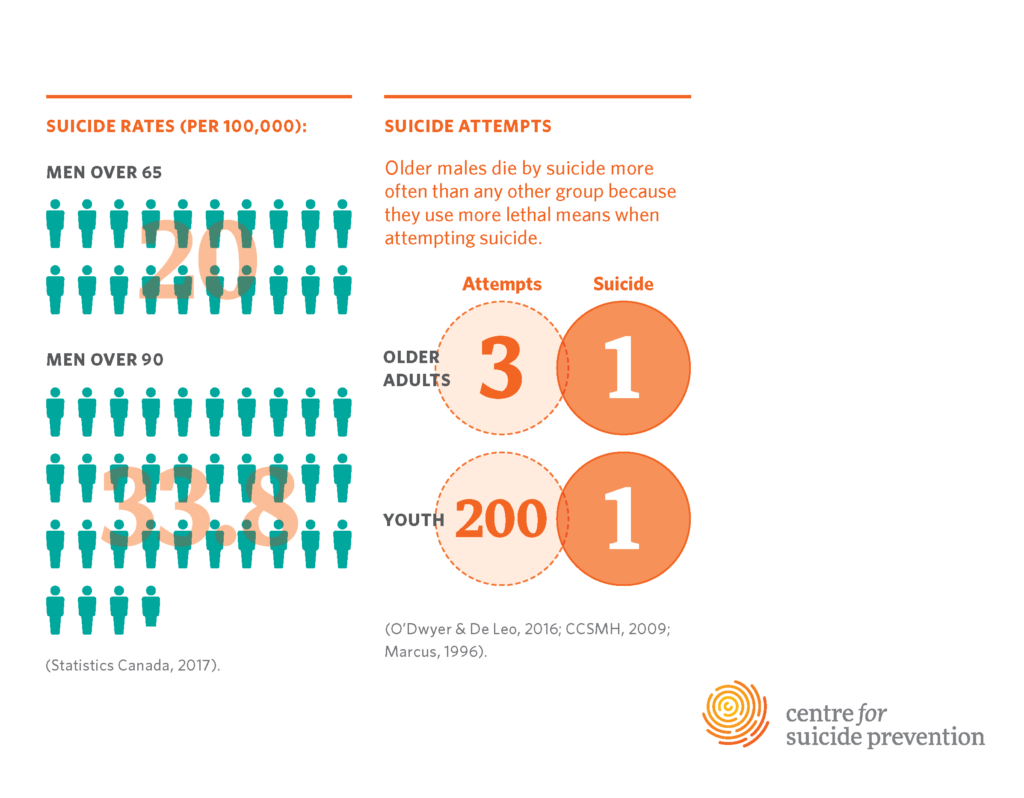
Suicide among older adults, especially those aged 75 and above, presents a significant public health challenge. Recent statistics indicate that this demographic experiences the highest suicide rates, estimated at 20.3 per 100,000 individuals, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Contributing factors include social isolation, which is prevalent among the elderly population, and underrepresentation in research concerning mental health resources. As communities seek to address the concerning rise in suicides among seniors, it becomes evident that tailored approaches are necessary to mitigate the unique challenges faced by this vulnerable group.
Furthermore, the dynamics of mental health in older adults are distinct from those in younger generations. The stigma surrounding mental health issues can deter older individuals from seeking help, exacerbating feelings of loneliness and despair. There is an urgent need for focused outreach and education to raise awareness about the mental health resources available for seniors and to foster an inclusive dialogue on geriatric suicide awareness. By understanding the risk factors and barriers older adults face, we can develop more effective suicide prevention strategies.
The Need for Targeted Suicide Prevention Resources for Seniors
Despite the alarming statistics surrounding elder suicide rates, current suicide prevention initiatives often overlook older adults, as highlighted in a recent study by researchers at McLean Hospital. The research reveals that national organizations focused on suicide prevention do not adequately provide resources tailored to the unique needs of the elderly. This inadequacy presents a significant gap in mental health support, especially given that older adults are increasingly turning to the internet to seek health information. Consequently, robust strategies must be developed that specifically address their healthcare needs and promote the availability of resources without added barriers.
As clinicians and researchers emphasize the necessity of public-facing campaigns, it is clear that to combat elder suicide effectively, strategies must be intentional and empathetic. These campaigns should aim to reach older adults in familiar environments, utilizing platforms they commonly use. This would include enhancing the visibility of mental health resources and ensuring that they are user-friendly for seniors facing technological challenges. By prioritizing accessible mental health resources, we can significantly impact the prevention of suicide among older adults.
Building Community Support for Elderly Mental Health
Community involvement plays a crucial role in bolstering suicide prevention efforts for older adults. It is essential to foster supportive social environments that help mitigate the risks associated with social isolation and loneliness. Programs that promote intergenerational interactions and community engagement can create meaningful connections that help seniors feel valued and understood. Local organizations and support groups can also serve as vital resources for older adults, providing them with the companionship and mental health support they often seek.
In addition, educating caregivers and loved ones about the signs of distress in older adults is essential for prevention. By equipping families and community members with the knowledge necessary to identify mental health concerns, we can empower them to intervene effectively before a crisis occurs. Initiatives that include workshops, training sessions, and informational campaigns dedicated to geriatric suicide awareness can play a pivotal role in transforming community perceptions about mental health challenges faced by seniors.
Leveraging Technology for Suicide Prevention in Older Adults
As older adults increasingly rely on technology to access information and resources, leveraging digital platforms could substantially enhance suicidal prevention efforts. Comprehensive online resources tailored for seniors can bridge the existing gap in mental health support. Websites that provide clear and straightforward information about suicidal behaviors can empower older adults to seek help proactively. Moreover, technology can facilitate virtual support groups, which may be less intimidating for some seniors compared to traditional in-person groups.
The integration of technology into mental health support for the elderly also opens avenues for real-time interventions. Apps and online services can offer easy access to screenings, crisis helplines, and chat services, enabling older adults to reach out for help without feeling vulnerable. By developing user-friendly digital mental health resources targeted at seniors, we can improve accessibility and engagement, making significant progress toward reducing suicide rates in this age group.
Increased Funding for Elderly Suicide Prevention Initiatives
To effectively combat the rising trend of suicide among older adults, increased funding is essential. Financial resources must be allocated toward research specifically focused on the unique aspects of mental health in seniors. Funding can support the development of tailored programs that address the social and emotional needs of older adults, ensuring they have access to crucial mental health services. Without a concerted effort to invest in this demographic, many seniors may continue to fall through the cracks of the existing healthcare system.
Moreover, financial support for grassroots organizations dedicated to elderly suicide prevention can amplify their impact. Community-based initiatives that create awareness about mental wellness among seniors and facilitate access to resources can help turn the tide. Encouraging investment in collaborative projects that engage various stakeholders—healthcare providers, mental health advocates, and community leaders—can establish a more comprehensive safety net for older adults at risk of suicide.
Encouraging Open Conversations About Mental Health
One of the significant barriers to seeking help for mental health issues among older adults is the stigma surrounding these discussions. Encouraging open conversations about mental health is crucial in creating an environment where seniors feel safe and supported when addressing their struggles. Public campaigns that normalize mental health conversations, particularly targeting older adults, can help alleviate stigma and create more supportive communities.
Additionally, presenting mental health as a vital component of overall wellness can encourage older adults to prioritize their emotional and psychological health. By fostering an environment where seeking help is regarded as an act of strength rather than weakness, older adults may be more likely to reach out for support when needed. Such proactive approaches can help create a culture of understanding and acceptance concerning elderly mental health challenges and the prevention of suicide.
The Role of Family and Caregivers in Prevention
Family members and caregivers play a pivotal role in the lives of older adults, especially regarding mental health. Being aware of the signs of depression or suicidal tendencies can equip caregivers to support their loved ones better. Regular check-ins and open discussions about mental health can create an atmosphere where older adults feel comfortable expressing their feelings without judgment. Family support systems can serve as a critical buffer against the risks of suicide by providing companionship and understanding.
Moreover, empowering caregivers with knowledge about local mental health resources can enhance their ability to provide appropriate support. Training sessions that educate families on recognizing mental health challenges and effective communication strategies will create a more informed, responsive network of care around older adults. Ultimately, the collaborative effort between families, communities, and healthcare professionals is vital to reducing the incidence of suicide among seniors.
Creating Culturally Competent Support Systems for Seniors
The diversity among the older adult population necessitates culturally competent mental health support systems. Understanding the unique cultural backgrounds and experiences of seniors is crucial in addressing their mental health needs effectively. Personalized approaches, considering cultural sensitivities, can facilitate more engaging and supportive mental health interventions. This tailored outreach can significantly enhance elderly suicide prevention efforts.
Additionally, training mental health professionals in cultural competence will ensure that they are equipped to understand and address the distinct challenges faced by older adults from various backgrounds. Programs that emphasize cultural awareness can cultivate an environment where seniors feel seen and validated in their experiences, thereby fostering greater openness in seeking help. By prioritizing culturally relevant resources in mental health, communities can significantly improve the effectiveness of suicide prevention efforts for older adults.
Developing Collaborative Networks for Mental Health Awareness
Collaborative networks involving various stakeholders—healthcare providers, mental health advocates, community organizations, and older adults—are fundamental for enhancing awareness about senior mental health issues. Such partnerships can leverage shared resources and expertise to create comprehensive outreach programs aimed at increasing awareness and availability of mental health resources for seniors. Coordinated efforts can lead to communal initiatives that ensure older adults are informed about the support available to them.
Initiatives that bring together diverse community sectors can also offer holistic solutions to prevent elder suicide. For example, workshops, training, and awareness campaigns that engage multiple stakeholders can promote a deeper understanding of the mental health challenges older adults face. Collaboration can turn the tide on how communities approach wellbeing for seniors, ensuring they feel supported and connected as they navigate mental health concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective mental health resources for elderly suicide prevention?
Effective mental health resources for elderly suicide prevention include hotlines tailored for older adults, community mental health support groups, and online counseling services that specialize in geriatric care. Organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) provide information, and the Suicide Prevention Lifeline offers access to trained professionals who understand the unique needs of seniors.
What can families do to support senior mental health and prevent suicide?
Families can play a crucial role in senior mental health support by maintaining open communication, encouraging social interaction, and keeping a watchful eye for signs of depression or suicidal thoughts. Engaging older adults in community activities and connecting them with mental health professionals can also help in suicide prevention.
What are the statistics on suicide rates in older adults?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), adults aged 75 and older experience one of the highest suicide rates at approximately 20.3 per 100,000 individuals. This statistic underscores the urgent necessity for focused elderly suicide prevention initiatives and accessible mental health resources.
Why is geriatric suicide awareness important in today’s society?
Geriatric suicide awareness is important because older adults are often subject to social isolation, depression, and healthcare disparities. Raising awareness can lead to better-targeted prevention efforts, help reduce stigma, and mobilize resources specifically designed to address the unique needs of this vulnerable population.
How can online platforms improve suicide prevention efforts for older adults?
Online platforms can enhance suicide prevention for older adults by making mental health resources more accessible, creating user-friendly interfaces, and offering information specifically tailored to their needs. Increasing visibility of resources and incorporating age-sensitive content will encourage older adults to seek help when needed.
What unique challenges do older adults face in accessing suicide prevention resources?
Older adults frequently face challenges such as limited mobility, lack of familiarity with technology, and feelings of stigma regarding mental health. These barriers can prevent them from accessing suicide prevention resources effectively, making it crucial to develop tailored outreach and support strategies.
What types of outreach campaigns are effective for elderly suicide prevention?
Effective outreach campaigns for elderly suicide prevention include community education programs that specifically target older adults, informational webinars, and partnerships with senior centers or healthcare providers. Campaigns should emphasize accessible mental health resources and encourage discussions about mental well-being within the community.
How does social isolation contribute to suicide rates in older adults?
Social isolation significantly contributes to suicide rates in older adults by exacerbating feelings of loneliness and depression. The lack of social support networks can lead to deteriorating mental health, highlighting the need for interventions focused on fostering connections and providing mental health resources tailored for seniors.
What role do local communities play in senior mental health support?
Local communities play an essential role in senior mental health support by providing social programs, behavioral health resources, and opportunities for engagement. Community-based initiatives can connect older individuals with peers, thereby reducing isolation and promoting mental well-being, ultimately contributing to suicide prevention.
How can healthcare providers better support mental health in older adults?
Healthcare providers can better support mental health in older adults by incorporating routine screenings for depression and suicidal ideation, ensuring accessibility of mental health resources, and offering comprehensive care that addresses the physical, emotional, and social factors affecting seniors. Training in geriatric psychiatry can further enhance provider effectiveness in suicide prevention.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Risk Population | Older adults aged 75 and older have the highest suicide rates (20.3 per 100,000) among all age groups. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations do not provide accessible resources specifically for older adults. |
| Imbalance in Targeting | Most online suicide prevention efforts are not aimed at older adults, despite their high risk. |
| Need for Tailored Strategies | There is an urgent need for targeted suicide prevention campaigns and tailored resources that address the unique healthcare needs of older adults. |
| Research Support | The study was funded by various institutions, highlighting the ongoing need for focused research on suicide prevention for older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue, as they represent the demographic with the highest risk of suicide. Despite this alarming statistic, current resources and online campaigns largely overlook their specific needs. Efforts must be directed towards creating accessible information and support tailored for this vulnerable population. By addressing the unique challenges they face, including social isolation and a lack of targeted resources, we can work towards reducing the suicide rates among older adults and ensuring their mental health needs are met.