Maternal mortality in the U.S. represents a critical public health crisis, as evidenced by the alarming rise in pregnancy-related deaths over recent years. Despite advancements in medical care, America leads all high-income countries in maternal mortality rate, with significant variations influenced by race and ethnicity. A study conducted from 2018 to 2022 highlights that heart disease has emerged as a leading cause of these fatalities, emphasizing the need to address postpartum care challenges faced by mothers. The disparities in maternal health outcomes, particularly among American Indian, Alaska Native, and Black women, point to deep-seated inequities within the healthcare system. To combat these rising rates, it is essential to invest in quality prenatal and extended postpartum care that can effectively address the unique needs of all mothers, reducing the staggering number of preventable deaths.
The issue of maternal mortality, often referred to as pregnancy-related fatalities, has gained increased attention in recent years, particularly regarding the challenges many women face during and after childbirth. With the United States grappling with the highest rates of these fatalities amongst affluent nations, it is crucial to explore the underlying factors contributing to this alarming trend. The concept of maternal health encompasses a broad spectrum of issues, including racial disparities in healthcare, complications such as cardiovascular disease during pregnancy, and insufficient postpartum support. These complexities indicate that maternal wellbeing is not merely about successful delivery but also involves addressing systemic biases and ensuring comprehensive care throughout the entire pregnancy continuum. As the nation campaigns for improved healthcare policies, the spotlight remains on how best to enhance maternal health outcomes and diminish the factors leading to preventable deaths.
The Rising Concern of Maternal Mortality in the US
Maternal mortality in the US has been a persistent issue, raising significant alarm among healthcare professionals and policymakers alike. As a high-income nation, the United States experiences a high maternal mortality rate compared to its peers, with over 80% of these deaths deemed preventable. Recent studies have shown a troubling upward trend in pregnancy-related deaths, particularly from 2018 to 2022. This alarming increase highlights systemic failures in prenatal care, postpartum healthcare, and overall maternal health management.
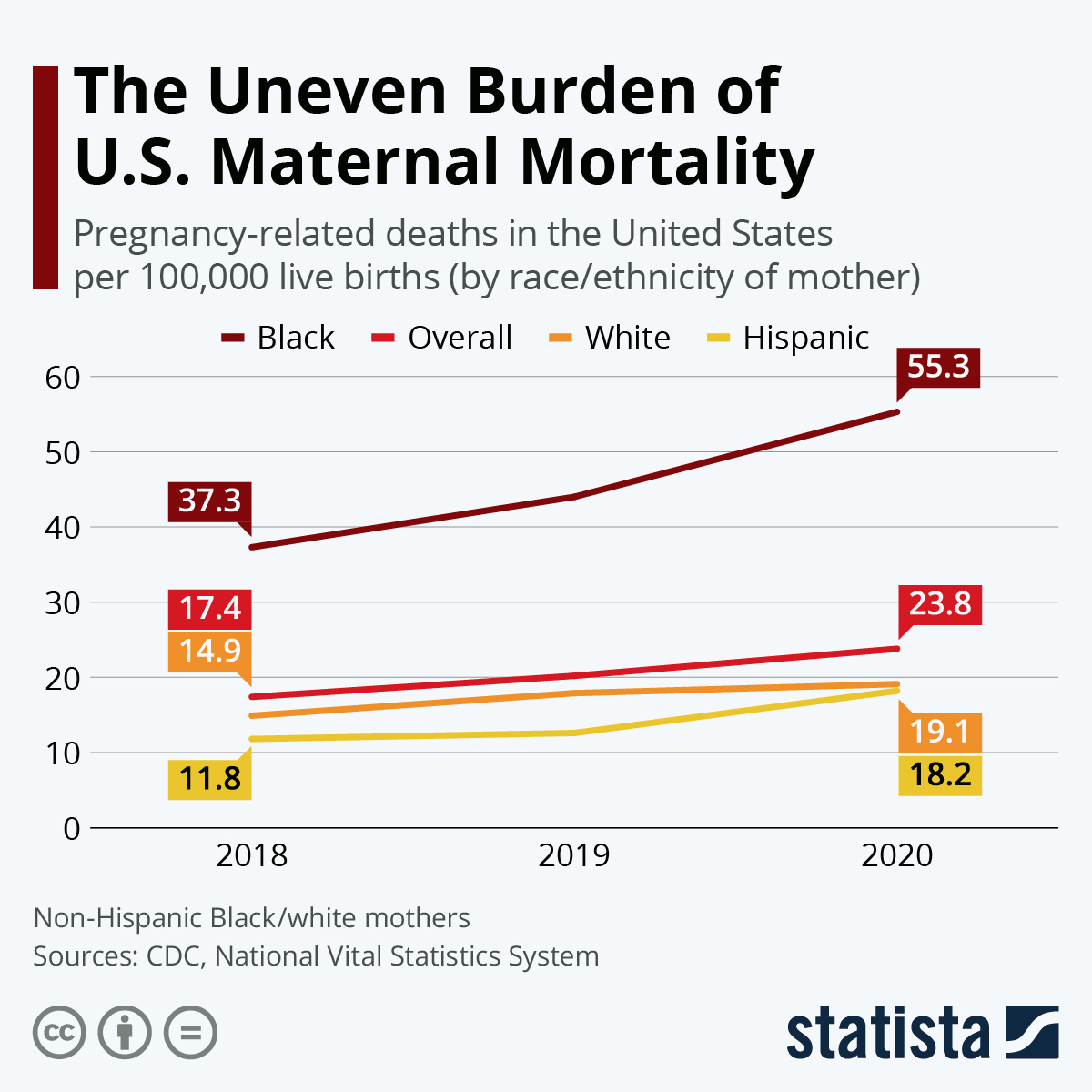
One contributing factor is the disparities in maternal mortality rates across different racial and ethnic groups. For example, American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest pregnancy-related death rates, which are almost four times greater than that of their white counterparts. This inequity calls for urgent reforms in healthcare delivery and policies that address the root causes of such disparities and work towards more equitable maternal health outcomes.
Understanding Racial Disparities in Maternal Health
The stark reality of maternal mortality lays bare the racial disparities that still plague the US healthcare system. Non-Hispanic Black and American Indian women experience mortality rates far exceeding those of white women, revealing deep-rooted biases and systemic inequities in healthcare access and treatment. Addressing these disparities is not just a matter of fairness; it’s essential for the health of future generations. As studies suggest, significant policy changes and targeted interventions are essential to improve outcomes for marginalized groups.
Policies aiming to reduce maternal deaths must focus on comprehensive healthcare access and culturally competent care. This involves training healthcare professionals to recognize and combat biases, as well as focusing on community-level interventions that connect women of color with resources during pregnancy and postpartum periods. By creating a more supportive environment for these communities, it is possible to make strides in closing the gap in maternal health outcomes.
The Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Maternal Mortality
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the United States, accounting for over 20% of such fatalities. This trend signifies a crucial shift in maternal health concerns, as conditions like hypertension and pre-eclampsia become increasingly prevalent among younger women. The contemporary increase in cardiovascular issues among the 25 to 39 age group hints at the vulnerability of reproductive-age individuals to chronic health problems, thus necessitating heightened awareness and proactive monitoring during pregnancy.
Understanding the link between cardiovascular health and maternal mortality emphasizes the need for integrated care models that prioritize both prenatal and postpartum health. Initiatives should focus on educating women about cardiovascular risks and ensuring regular screenings throughout their reproductive years. Furthermore, healthcare providers must adopt a holistic approach to maternal care, addressing not only immediate pregnancy health concerns but also long-term cardiovascular wellness.
Challenges in Postpartum Care for New Mothers
Postpartum care challenges represent a critical dimension of maternal health that is often overlooked. The traditional healthcare model often neglects the importance of ongoing support beyond the initial six weeks post-birth. With late maternal deaths — defined as those occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum — constituting nearly a third of all maternal deaths, it is evident that the postpartum period requires a more sustained focus within healthcare systems.
To combat high rates of postpartum mortality, healthcare providers must create comprehensive follow-up strategies that extend beyond standard checkups. This includes mental health support, chronic disease management, and continuous education on maternal health. Ultimately, improving postpartum care is vital in ensuring women recover fully and address any lingering health issues that could threaten their well-being.
Policy Implications of Rising Maternal Mortality Rates
The rising maternal mortality rates in the United States necessitate comprehensive policy reforms to address the multiple factors contributing to these deaths. Policymakers must explore systemic issues within healthcare delivery, including the availability of services in maternity care deserts, insurance coverage for maternal health, and systemic biases affecting care quality. Implementing policies that prioritize maternal health can help reduce unnecessary pregnancy-related deaths.
Furthermore, the data indicating state-level variations in maternal mortality rates should guide targeted state-specific initiatives. By examining the successful strategies in states with lower rates, lawmakers can adapt these models to improve care in others. Collaboration between various stakeholders, including healthcare leaders and community organizations, is crucial to develop effective policies that ensure equitable and safe maternal healthcare across the nation.
Integrating Mental Health into Maternal Care
Mental health is an integral aspect of maternal well-being, yet it often remains under-addressed in prenatal and postpartum care. Conditions such as postpartum depression can dramatically affect both mother and child, yet many women do not receive adequate mental health support during this crucial period. Recognizing the mental health needs of new mothers and integrating mental health services into maternity care can reduce the risk of maternal mortality and improve long-term outcomes for both mothers and their infants.
To effectively address mental health within maternal care, healthcare providers should screen for psychological conditions during and after pregnancy. Developing support systems and referral networks that connect mothers with mental health resources will also empower them to seek help when needed. By prioritizing mental wellness, we can contribute to a more holistic approach to maternal health that encompasses physical, emotional, and psychological well-being.
The Impact of Healthcare Accessibility on Maternal Mortality
Healthcare accessibility is a significant factor influencing maternal mortality rates in the US. In many areas, particularly rural or underserved communities, access to comprehensive maternity care remains limited. This lack of access can lead to delayed prenatal care, inadequate monitoring of pregnancy complications, and insufficient postpartum support, all of which contribute to higher mortality rates among mothers. Ensuring that all women have access to quality maternal healthcare is fundamental in addressing this crisis.
Improving healthcare accessibility requires innovative solutions such as telemedicine, which provides remote consultations and can help mothers in remote areas receive essential care without the need for long travels. Additionally, expanding insurance coverage and protective policies tailored to pregnant women can significantly mitigate barriers to access. Ultimately, addressing these issues will create a more equitable landscape for maternal care throughout the United States.
Innovative Solutions to Reduce Pregnancy-Related Deaths
In light of the alarming rise in pregnancy-related deaths, innovative solutions are essential to shift the trend towards safer maternal health outcomes. Emphasizing preventive care, healthcare systems can implement measures such as regular screening for chronic conditions and immediate interventions for high-risk pregnancies. Expanding community health programs that educate and provide resources to expectant and new mothers can also play a critical role in reducing mortality rates.
Moreover, investment in healthcare technology, such as data analytics and health monitoring applications, can enhance maternal care by offering real-time insights into patients’ health. By fostering collaborations between healthcare providers, researchers, and community leaders, we can drive forward innovative solutions that prioritize the health and well-being of mothers across diverse communities.
The Importance of Maternal Health Advocacy
Advocacy for maternal health is crucial in addressing the systemic issues contributing to rising maternal mortality rates in the US. Engaging communities and advocating for policies that promote reproductive health access, comprehensive maternity care, and education on maternal health can help elevate awareness and accountability within our healthcare systems. By encouraging public discourse around the challenges faced by mothers, we can create compelling reasons for policy shifts and healthcare reforms.
Grassroots organizations and maternal health advocates play a vital role in championing the needs of women, especially those in marginalized populations disproportionately affected by high maternal mortality rates. Strengthening advocacy efforts can drive legislative change that promotes health equity and improves outcomes for all mothers. Sustained attention to maternal health advocacy is essential to ensure that future generations of women receive the care and respect they deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the maternal mortality rate in the US and how does it compare internationally?
The US has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with an alarming increase from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to 32.6 in 2022. This rate highlights significant challenges in addressing pregnancy-related deaths compared to peers globally.
What are the primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the US?
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the US, accounting for over 20% of such fatalities. Other causes include hemorrhage and complications related to chronic conditions such as hypertension and diabetes.
Why do racial disparities in maternal health exist in the US?
Racial disparities in maternal health in the US are largely due to systemic inequities within the healthcare system, including access to quality prenatal care and postnatal support. American Indian and Alaska Native women, for example, experience nearly four times higher mortality rates than white women.
How significant are postpartum care challenges in reducing maternal mortality?
Postpartum care challenges are crucial to addressing maternal mortality, as nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and a year after birth. Improved postpartum care can significantly reduce these preventable deaths and improve overall maternal health outcomes.
What role does cardiovascular disease play in maternal mortality in the US?
Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of maternal mortality in the US, reflecting a growing prevalence of chronic conditions like hypertension among younger pregnant individuals. More attention is needed to manage these health risks during pregnancy.
What are the implications of the rising maternal mortality rates in the US?
The rising maternal mortality rates in the US indicate a need for urgent reform in healthcare policies and practices. Addressing these rates requires investment in public health infrastructure and a focus on equitable access to quality care during and after pregnancy.
How can the US improve outcomes related to maternal mortality?
To improve outcomes related to maternal mortality, the US needs to invest in healthcare infrastructure, enhance access to education about pregnancy-related health issues, and ensure comprehensive care extends beyond the immediate postpartum period to tackle challenges faced by new mothers effectively.
What measures are being taken to track pregnancy-related deaths in the US?
Since 2018, the US has improved tracking of pregnancy-related deaths through the implementation of a pregnancy checkbox on death certificates. This system allows for better data collection and understanding of maternal mortality trends, though continued investment in public health research is essential.
Why is it important to consider ‘late maternal deaths’ in maternal mortality statistics?
Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum, are crucial to consider as they highlight the need for extended care beyond the traditional six-week period, underscoring gaps in healthcare services for new mothers.
What strategies can help address the high maternal mortality rates in the US?
Strategies to address high maternal mortality rates include promoting equitable access to quality healthcare, enhancing prenatal and postpartum care services, and implementing policies focused on reducing racial disparities in maternal health outcomes.
| Key Points | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Leads in Maternal Mortality | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries. | |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. | |
| Rising Mortality Rates | Rates rose from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to 32.6 in 2022, with notable increases during the COVID-19 pandemic. | |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates, with significant differences across racial groups. | |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease leads as a cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20%. | |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (up to 1 year postpartum) account for almost a third of mortality cases. | |
| Need for Policy Changes | Calls for improved healthcare systems, particularly in postpartum care and addressing policy inequities. | |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the US is a critical public health issue that continues to escalate, with a need for urgent intervention and policy reform. Despite over 80% of these deaths being preventable, the rates have risen significantly in recent years, particularly affected by disparities based on race and ethnicity. The focus must shift toward extending postpartum care and addressing systemic inequities in healthcare to reduce these alarming statistics.